Your ADS
What is Geographic Coordinate Symbol?
Latitude and longitude in a geographic coordinate system.
To specify any location on the globe, you have to find its latitude (parallel) and longitude (meridian). Latitudes and longitudes can be visualized as an array of imaginary lines running along Earth’s surface. A position is measured in angle units: degrees (°), minutes of arc ('), and seconds of arc ("). Each degree is subdivided into 60 minutes of arc, which in turn are subdivided into 60 seconds of arc. Sometimes decimal degrees are used instead of minutes and seconds of arc, or decimal minutes instead of seconds of arc. For example, 156°16'21" = 156°16.35' = 156.2725°.
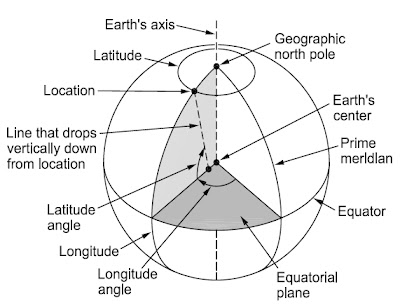
The latitude of a location is defined as the angle between the equatorial plane and an imaginary line that drops vertically down from the location. This line generally does not intersect the equatorial plane exactly at Earth’s center because Earth’s surface is slightly flattened at the poles. The latitude is a measure of how far north or south a location is from the equator. Latitudes can be visualized as a series of concentric circles centered on the geographic poles and expanding to a maximum radius at the equator.
To specify the latitude, state the latitude angle and whether the position is north (N) or South (S) of the equator. The latitude is 90°N at the North Pole, 0° at the equator, and 90°S at the South Pole. Other locations have intermediate latitudes, for example, 46°25'09"S. The length along Earth’s surface of one minute of latitude is proportional to the radius of curvature along the local surface; it varies from 1843 m at the equator to 1862 m at the poles. The original definition of the nautical mile was the average distance of one minute of arc of latitude along Earth’s surface. Today, the nautical mile is defined as precisely 1852 m.
 |
| How Latitudes and Longitudes are Derived |
The longitude of a location is defined as the angle, parallel to the equatorial plane, between the location and a reference longitude called the prime meridian. By convention, the prime meridian (0°) is the longitude that runs through an established point at Greenwich, England. From there, other longitudes increase eastward and westward until they meet at 180° on the opposite side of Earth. The longitude is thus a measure of how far east (E) or west (W) a location is from the prime meridian.
Longitudes can be visualized as a series of north-south lines that converge at the poles. To specify the longitude, state the longitude angle and whether the position is east or west of the prime meridian, for example, 105°57'15"E. The length along Earth’s surface of one minute of longitude varies from 1855 m at the equator to 0 at the geographic poles.
